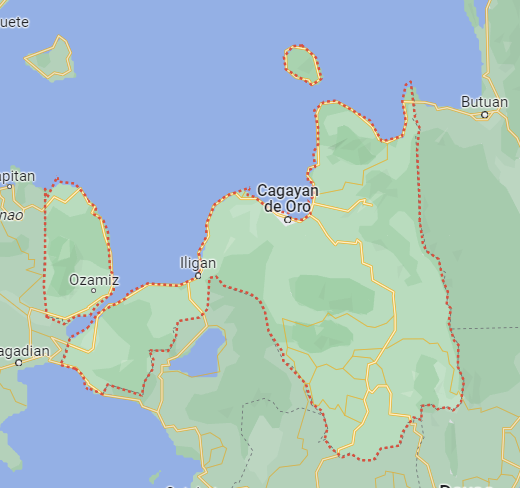
Northern Mindanao, officially designated as Region 10, is a vibrant and diverse administrative region in the Philippines. Nestled in the northern part of the island of Mindanao, it is a region known for its rich cultural tapestry, stunning landscapes, and rapidly growing economy. This article delves into the heart of Northern Mindanao, exploring its geography, culture, and economic significance.
Quick Summary:
- Land Area: 20,186 sq km
- Population as of 01 May 2020: 5,022,768
- Regional Center: Cagayan De Oro City
- 5 provinces of Region 10: Camiguin, Bukidnon, Lanao Del Norte, Misamis Occidental, and Misamis Oriental.
- 2 highly urbanized cities: Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City.
- Consists of 84 municipalities and 2,022 barangays.
Geography and Demographics
Northern Mindanao encompasses a land area of 20,186 square kilometers, making it one of the larger regions in the Philippines. As of the 2020 census, it was home to approximately 5,022,768 people.
The region is divided into five provinces: Camiguin, Bukidnon, Lanao Del Norte, Misamis Occidental, and Misamis Oriental. These provinces contribute to the rich cultural diversity and economic activities that shape Northern Mindanao.
Also Read: List of Regions in the Philippines
Region 10 Provinces List
| Province | Capital |
| Bukidnon | Malaybalay City |
| Camiguin | Mambajao |
| Lanao del Norte | Tubod |
| Misamis Occidental | Oroquieta City |
| Misamis Oriental | Cagayan de Oro City |
Urban Centers and Regional Center
Northern Mindanao boasts two highly urbanized cities: Cagayan de Oro City and Iligan City. Cagayan de Oro City serves as the regional center and a hub of commerce, culture, and administration for the region. The two cities are vital players in the region’s economic development and growth.
Region 10 Cities
9 Cities in Northern Mindanao
1. Malaybalay City
2. Valencia City
3. Iligan City
4. Oroquieta City
5. Ozamiz City
6. Tangub City
7. Cagayan de Oro City
8. El Salvador City
9. Gingoog City
Religion and Culture
The predominant religion in Northern Mindanao is Roman Catholicism, with approximately 72% of the population adhering to this faith. However, there are also significant populations of Protestants and Muslims, contributing to the region’s religious diversity.
The cultural fabric of Northern Mindanao is rich and diverse, with a multitude of dialects spoken. Cebuano, Maranao, Hiligaynon, Subanon, Bukid, Kamigin, Ilianen, Matigsalug, and Iranun are just a few of the languages spoken in the region. Many of its inhabitants can trace their ancestry back to Cebu and Bohol, highlighting the historical migration patterns that have shaped Northern Mindanao.
In 2001, Lanao Del Norte was transferred to Northern Mindanao from Region 12, marking a significant administrative change.
Etymology
The name “Northern Mindanao” was officially coined during the American colonial period, following the establishment of American rule in the Philippines. It was chosen, in part, due to the suppression of Filipino revolutionaries who had fought for independence from Spanish colonial rule.
Interestingly, there have been other proposals to change the region’s name. “Amihanan Region,” meaning “Northern Area” in Cebuano, and “CALAMINON,” an acronym formed from the region’s provinces, have been suggested as alternatives.
Economy and Industry
The economy of Northern Mindanao is primarily based on agriculture, forestry, fishing, and hunting. It is an important agricultural region in the Philippines, producing top commodities such as bananas, pineapples, chickens, hogs, and corn. These products are not only staples in the local diet but are also significant contributors to the national agricultural output.
Moreover, the region plays a crucial role in the energy sector. The Agus-IV to VII Hydroelectric Plants in Iligan and Balo-i, Lanao del Norte, supply a substantial portion of the electrical power in Mindanao. This has helped meet the energy demands of the region and neighboring areas.
In recent years, Northern Mindanao has experienced a boom in industrial and manufacturing sectors, particularly in Iligan and Cagayan De Oro. These cities have become centers of commerce and industry, offering employment opportunities and contributing to the region’s economic development.
Conclusion
Northern Mindanao, or Region 10, is a region of great significance in the Philippines. With its cultural diversity, agricultural prowess, and rapidly growing economy, it plays a vital role in the nation’s development. As the region continues to evolve and embrace new opportunities, Northern Mindanao promises to be a dynamic and exciting part of the country.
Northern Mindanao Quickstats
| INDICATORS | DATA |
| Population (2020) | 5,022,768 |
| Land Area (2010) | 20,186 sq km |
| Provinces | 5 |
|---|---|
| Cities | 9 |
| Municipalities | 84 |
| Barangays | 2,022 |
| Coastal/Landlocked | coastal |
| Marine waterbodies | Bohol Sea, Celebes Sea |
| Density (2020) | 246 / km2 (636 / sq mi) |
| Island Group | Mindanao |